LeetCode记录①
在LeetCode学习的记事本。

141. 判断一个链表是否含有环形结构
141.Linked List Cycle
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer
poswhich represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. Ifposis-1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
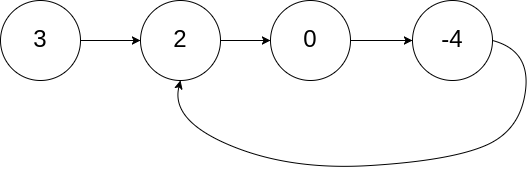
解题思路
-
使用hash表存储访问过的节点,如果发现节点已经在表中,则表示链表含有环形结构。
-
使用快慢指针,当快指针与慢指针相遇时,表示链表中存在环形结构。
代码
java
//141 hashSet方式
public boolean hasCycle1(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> nodeSet = new HashSet<>();
while (head != null) {
if (nodeSet.contains(head)) {
return true;
} else {
nodeSet.add(head);
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
//141 快慢指针方式
public boolean hasCycle2(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = slow;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
golang
//141 map方式 存储的K是节点地址 v可以是任意值
func hasCycle1(head *ListNode) bool {
nodeMap := make(map[*ListNode]int)
node := head
for node != nil {
if _, ok := nodeMap[node]; ok {
return true
} else {
nodeMap[node] = 1
}
node = node.Next
}
return false
}
//141 快慢指针方式
func hasCycle2(head *ListNode) bool {
slow := head
fast := head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
if slow == fast {
return true
}
}
return false
}
142. 找出链表中环结构的起点
142.Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return
null.To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer
poswhich represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. Ifposis-1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.Note: Do not modify the linked list.

解题思路
-
使用hash表存储访问过的节点,返回第一个与表中重复的节点。
-
使用快慢指针,当快指针与慢指针相遇时,相遇点与环形结构起点的距离,刚好等于
head链表头节点到环形结构起点的距离。利用这一点,在第一次相遇时,让快指针再次从head开始,以与慢指针同样的速度前进,同时慢指针继续从相遇点原速前进,则接下来的相遇点即为所求的环形结构起点。- 这样说可能有些抽象,我下面画图说明:
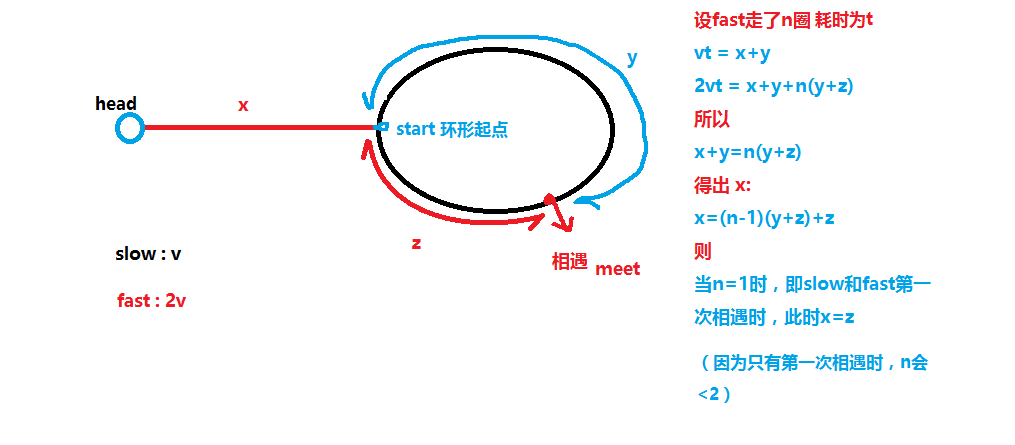
假设有两个运动员
slow和fast,slow的速度为v,fast的速度是slow的2倍为2v,两人从head点开始通过一段长为x的直道,最后进入环形跑道做匀速运动,设两人相遇点为meet处,设环形跑道的周长C为y+z,可以得出x=kC+z,其中k为自然数。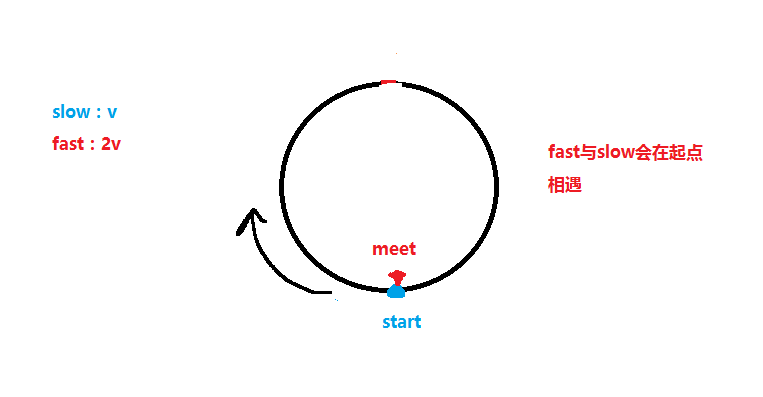
如果没有直道,相遇点就会一直是起点,也可以说明上面的推论是正确的。
代码
java
//142 hashSet方式略
//142 快慢指针方式
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = slow;
while (true) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return null;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
break;
}
}
fast = head;
while (fast != null) {
if (fast == slow) {
return slow;
}
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return null;
}
golang
//142 hash表方式略
//142 快慢指针方式
func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
slow := head
fast := slow
for {
if fast == nil || fast.Next == nil {
return nil
}
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
if slow == fast {
break
}
}
fast = head
for fast != nil {
if fast == slow {
return fast
}
fast = fast.Next
slow = slow.Next
}
return nil
}
78. 找出一个集合的所有子集
78.Subsets
Given a set of distinct integers, nums, return all possible subsets (the power set).
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
Example:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output:
[
[3],
[1],
[2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[]
]
解题思路
-
迭代,从每轮子集中寻找规律
-
结果集初始为
{},第一轮为{},{1},第二轮为{},{1},{2},{1,2},可以得出:每轮结果都是对上一轮中所有集合的扩充。对所有上轮集合都添加1个当前元素,然后把此轮得到的集合,合并到结果集。 -
将结果集命名为
allList,我在下图解释了第二轮集合的获取方式: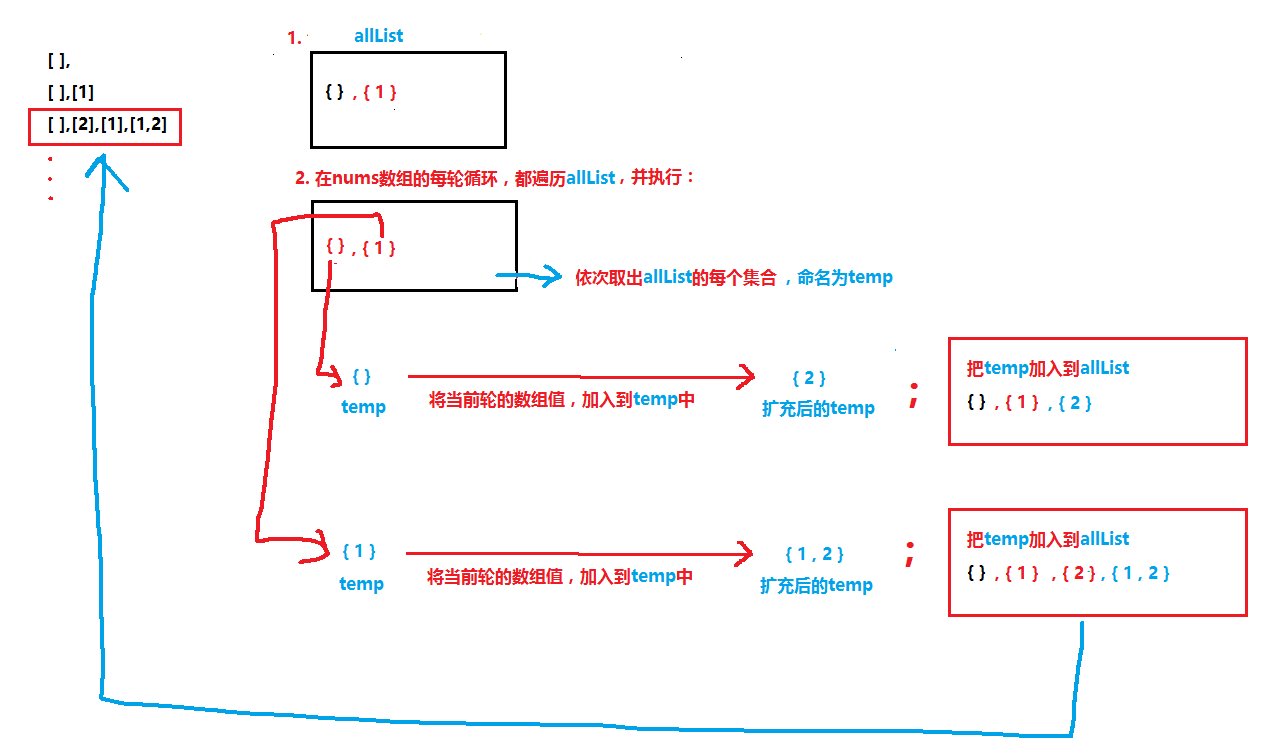
-
-
递归回溯,常用的方法,我在90题也使用了同样的方法。
代码
java
//78. 迭代方式
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> allList = new ArrayList<>();
allList.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int value : nums) {
for (int p = 0, size = allList.size(); p < size; p++) {
List<Integer> temp = new LinkedList<>(allList.get(p));
temp.add(value);
allList.add(temp);
}
}
return allList;
}
}
//78. 递归
public List<List<Integer>> subsets2(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> allList = new LinkedList<>();
backStack(nums, 0, new LinkedList<>(), allList);
return allList;
}
private void backStack(int[] nums, int start, List<Integer> list, List<List<Integer>> allList) {
allList.add(new LinkedList<>(list));
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
list.add(nums[i]);
backStack(nums, i + 1, list, allList);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
}
}
//90. 78然后去重
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> allList = new LinkedList<>();
//排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
backStack2(nums, 0, new LinkedList<>(), allList);
return allList;
}
private void backStack2(int[] nums, int start, List<Integer> list, List<List<Integer>> allList) {
allList.add(new LinkedList<>(list));
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
//去重
if (i > start && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
list.add(nums[i]);
backStack2(nums, i + 1, list, allList);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
}
}
golang
//78 迭代方式
func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
all := [][]int{{}}
for _,value := range nums{
for _,temp := range all{
temp = append([]int{value}, temp...)
all = append(all, temp)
}
}
return all
}
//78 递归
func subsets2(nums []int) [][]int {
var allList [][]int
backStack(nums,0,[]int{},&allList)
return allList
}
func backStack(nums []int, start int, list []int, allList *[][]int) {
*allList = append(*allList, list)
for i := start; i < len(nums); i++ {
list := append([]int{nums[i]}, list...)
backStack(nums, i+1, list, allList)
list = list[len(list)-1:]
}
}
//90. 78然后去重
func subsetsWithDup(nums []int) [][]int {
var allList [][]int
sort.Ints(nums)
backStack2(nums, 0, []int{}, &allList)
return allList
}
func backStack2(nums []int, start int, list []int, allList *[][]int) {
*allList = append(*allList, list)
for i := start; i < len(nums); i++ {
//排序
if i > start && nums[i] == nums[i-1]{
continue
}
//去重
list := append([]int{nums[i]}, list...)
backStack2(nums, i+1, list, allList)
list = list[len(list)-1:]
}
}
349. 两个数组的交集
349.Intersection of Two Arrays
Given two arrays, write a function to compute their intersection.
Example:
Input: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
Output: [9,4]
这题应该是考集合的使用,使用set或者map都是可以的,第350题也大致相同。
java
//349. Intersection of Two Arrays
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int num1 : nums1){
set.add(num1);
}
int min = Math.min(nums1.length,nums2.length);
int[] arr = new int[min];
int p = 0;
for (int num2 : nums2){
if(set.contains(num2)){
arr[p] = num2;
p += 1;
set.remove(num2);
}
}
return Arrays.copyOf(arr,p);
}
//350. Intersection of Two Arrays II
public int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int num1 : nums1) {
//下面这段可以用map.merge()方法表示 map.merge(num1, 1, Integer::sum);
Integer value = map.get(num1);
if (value != null) {
map.put(num1, value + 1);
} else {
map.put(num1, 1);
}
}
int min = Math.min(nums1.length, nums2.length);
int[] arr = new int[min];
int p = 0;
for (int num2 : nums2) {
Integer value = map.get(num2);
if (value != null && value > 0) {
arr[p] = num2;
p += 1;
map.put(num2, value - 1);
}
}
return Arrays.copyOf(arr, p);
}
golang
//349. Intersection of Two Arrays
func intersection(nums1 []int, nums2 []int) []int {
aMap := make(map[int]int)
for _, num1 := range nums1 {
aMap[num1] = 1
}
var res []int
for _, num2 := range nums2 {
if _, ok := aMap[num2]; ok {
res = append(res, num2)
delete(aMap,num2)
}
}
return res
}
//350. Intersection of Two Arrays II
func Intersect(nums1 []int, nums2 []int) []int {
aMap := make(map[int]int)
for _, num1 := range nums1 {
//若map[int]int无此键 value为0
if value := aMap[num1]; value > 0 {
aMap[num1] = value + 1
} else {
aMap[num1] = 1
}
}
var res []int
for _, num2 := range nums2 {
if value := aMap[num2]; value > 0 {
res = append(res, num2)
aMap[num2] = value - 1
}
}
return res
}